The Importance of First-Party Data in the Shift of Google's Advertising Strategy
Published: Nov 17, 2025|12 min read|
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Present State of Google Ads, Transformed by AI and Privacy
- Chapter 1: How Will Advertising Change with the Reduction of Third-Party Cookies? 🍪
- Chapter 2: Google is Shifting to Its Own Properties: Reconfirming the GDN's Position
- Chapter 3: The Stars of AI Campaigns: Differentiating PMax and Demand Gen 🚀
- Chapter 4: Google Strengthens "Completion Within Its Own Walls": AI Overview and Revenue Structure Changes 💰
- Chapter 5: The Winning Strategy is Building a 1PD Foundation: Execution Steps for Measurement, Audience, and Integration 📊
- Conclusion: Investing in a CDP is the Shortest Route to Improving Results 💡
- Terminology
- Contact Us / Ask a Question
Introduction: The Present State of Google Ads, Transformed by AI and Privacy
The world of digital marketing is facing two historic turning points: the dramatic evolution of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and the global trend toward user privacy protection. To adapt to this change, Google Ads has completely shifted its central axis to a new campaign structure that maximizes automation and data utilization. AI-powered solutions like Performance Max (PMax) and Demand Generation (Demand Gen) have become the mainstay for advertisers to maximize results across the entire Google ecosystem.
This article aims to understand this wave of change and analyze how the positioning of the Google Display Network (GDN) has specifically shifted. The GDN was once a crucial pillar for advertising agencies, but its role has been significantly redefined in line with Google's AI strategy and the shift toward first-party data (1st Party Data).
As an advertising agency, we continue to utilize the GDN as one of our proposed channels. This paper acknowledges the historical significance of the GDN and focuses on strategies to maximize its potential. We will explain the first-party data utilization strategies essential for advertisers to maintain competitiveness in this new era, and the data infrastructure development required to support it.
Chapter 1: How Will Advertising Change with the Reduction of Third-Party Cookies? 🍪
Third-party cookies (TPCs), the long-standing foundation of digital advertising, enabled cross-website user tracking, personalized targeting, and high-precision ad measurement.
However, with the strengthening of privacy regulations such as Europe's GDPR and the US's CCPA, coupled with major browsers like Apple Safari and Mozilla Firefox beginning to block TPCs by default, their functionality has been diminishing.
Google's original plan to phase out TPCs in Chrome, which holds the majority of market share, was expected to have an immense impact on the entire digital advertising industry. Research indicated that if TPC use were banned, publisher revenue was estimated to decrease by about 30%. In response to this potential market disruption, the UK's Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) held competition concerns, fearing that Google's removal of TPCs could restrict functionality for competitors and favor its own online advertising services.
This very trend of privacy protection 🔒 became the biggest factor compelling companies to re-evaluate TPC-independent first-party data (1st Party Data) as a strategic asset.
Chapter 2: Google is Shifting to Its Own Properties: Reconfirming the GDN's Position
The Google Display Network (GDN) is one of the world's largest advertising networks provided by Google, including over 2 million websites and mobile apps, and it is a vast platform capable of reaching over 90% of internet users worldwide. The GDN was born in March 2003 as the Google Content Network.
While the early GDN was mainly text-based ads, its technological foundation was strengthened by the acquisition of DoubleClick in 2007, enabling it to support diverse ad formats such as images, videos, and rich media. The history of the GDN has greatly contributed to the development of the entire web, serving as a "savior" to monetize countless page views that couldn't prepare their own ad servers. The GDN made it possible to deliver ads to the appropriate audience through various methods, including demographics, interests, contextual targeting, and remarketing.
In the past, the GDN was a vital advertising channel for many advertisers, leveraging its vast reach to improve brand awareness and for remarketing (re-engagement). We, as advertising agencies, also made full use of this extensive inventory.
Driven by technological advancements and strategic shifts within Google, the GDN's role and value are being redefined, opening up new opportunities for advertisers
First, in July 2024, Google temporarily paused its plan for the phased deprecation of TPCs in Chrome, and subsequently, in April 2025, it also canceled the plan to introduce a standalone prompt (an independent choice) to restrict TPC use. This gave the digital advertising industry a temporary reprieve of TPC survival. The CMA (Competition and Markets Authority) also determined that since TPC use would be maintained, the competition concerns premised on TPC deprecation were resolved.
However, even if the threat of TPC deprecation has temporarily receded, the strategic transformation of Google's advertising business has not stopped. Google is strengthening its focus on its own properties (Google Services) such as Search, YouTube, Gmail, and Discover, due to their high profitability and ease of data quality management. 💸
Ad revenue generated via Google Network Properties (GDN's external sites) incurs Traffic Acquisition Cost (TAC), which is the distribution of ad revenue to media partners. For this reason, the GDN has a financial aspect of lower profitability compared to Google's own properties like YouTube and Search.
In fact, the financial reports of Google's parent company, Alphabet, also show that the revenue composition is shifting from network properties to its own properties.
Quoted Section: https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1652044/000165204424000022/goog-20231231.htm
Source (Japanese): "The TAC rate decreased from 21.8% in 2022 to 21.4% in 2023, primarily due to a shift in revenue composition from Google network properties to Google search and other properties."
Thus, Google is concentrating its resources on an environment where it can leverage its more profitable and more manageable first-party data (1PD).
Chapter 3: The Stars of AI Campaigns: Differentiating PMax and Demand Gen 🚀
As of 2025, Google Ads champions "AI-first," with the evolution of AI transforming everything from ad creation to budget allocation. Google automatically optimizes ads when advertisers input goals, creatives, and especially audience signals (1st Party Data) into the AI.
The core of this AI strategy is Performance Max (PMax) and Demand Generation (Demand Gen) campaigns.
- 🎯Performance Max (PMax): PMax is an AI solution provided by Google, designed to maximize conversions across all of Google's advertising channels, including Search, Display, YouTube, Shopping, and Gmail. The key to PMax's success lies in supplying high-quality data (1PD) provided by the advertiser as signals to the AI, thereby shortening the learning period.
- 📈Demand Generation (Demand Gen): Demand Gen (Demagen) aims to stimulate demand and drive conversions, focusing on visually immersive Google properties like YouTube, Discover, and Gmail. While PMax covers all channels, Demand Gen focuses on targeting control and pushing users into the middle stage of the funnel (consideration).
In the past, Demand Gen was clearly separated from the GDN and was a campaign delivered primarily only on Google's "own" properties. This design was intended to avoid the TAC (low profitability) of third-party networks like the GDN and technical tracking challenges.
However, currently, the GDN inventory itself is being integrated as a function of Demand Gen campaigns. This integration signifies a major change.
- ✅The New Standard for Display Ads: Since around March 2025, Demand Gen campaigns have effectively merged with the GDN, transforming into an integrated campaign that can deliver almost all display-type ad placements available on Google. Consequently, while traditional standalone display campaigns (GDN-specific campaign types) continue to exist, their functionality is now largely encompassed and optimized within Demand Gen, making the integrated approach the more effective and comprehensive choice for modern display advertising.
- ✅Addition of Management Functions: Demand Gen has seen the addition of an unusual "management" function for automation-mainstream Google Ads, allowing channel management at the ad group level for placements including the GDN (since March 2025).
- ✅Redefinition of GDN's Role: The GDN has maintained its vitality and evolved, becoming a vast inventory source for more advanced, AI-driven campaigns like PMax and Demand Gen. When proposing the GDN as an advertising agency, offering it as part of Demand Gen or PMax, which utilizes this vast reach more efficiently through AI optimization logic, is becoming the modern standard.
Chapter 4: Google Strengthens "Completion Within Its Own Walls": AI Overview and Revenue Structure Changes 💰
The primary revenue source for Google's parent company, Alphabet, remains the Google Services segment (Search, Advertising, YouTube, etc.), which is its most profitable business. In the latest financial results (Q3 2025), Alphabet surpassed $100 billion in quarterly revenue for the first time, with its main businesses of Search, YouTube, and Cloud achieving double-digit growth driven by AI.
Behind this growth is a fundamental shift in Google's strategy to smartly utilize the first-party data (1PD) enclosed within its own properties.
Convergence of Advertising Business Models
Traditional Google Search operated with an open stance of "guiding users to external websites as quickly as possible." However, with the increase of its own massive properties like YouTube and Google Maps, and the evolution of AI, Google's basic thinking has changed to a policy of "having users stay on Google properties as long as possible."
This signifies that Google is following the business models of social media platforms like Meta and TikTok, which maximize profits by having users navigate content within their own platforms.
Symbolizing this move is the introduction of the AI-powered search experience, "AI Overview (AIO)" 🤖. AIO displays an AI-generated summary answer at the top of the search results, increasing "zero-click searches" where users find information completion within Google without clicking links.
Quoted Section: State of Search Q1 2025: Behaviors, Trends, and Clicks Across the US & Europe | Datos Datos
Source (Japanese): "Roughly summarizing, the increase in 'inflow to Google properties' and 'zero-clicks' is extending the time spent and frequency of use within the world Google manages, and in turn, 'inflow to organic,' which is the pathway to the open internet, is decreasing."
As a result, the frequency of use in "the world Google manages" is growing, strengthening the structure that feeds back into Google's revenue. Traffic to the open internet, including the GDN, is on a downward trend, and Google's AI-driven campaigns (PMax, Demand Gen) are optimized for this "walled-garden" customer experience.
Chapter 5: The Winning Strategy is Building a 1PD Foundation: Execution Steps for Measurement, Audience, and Integration 📊
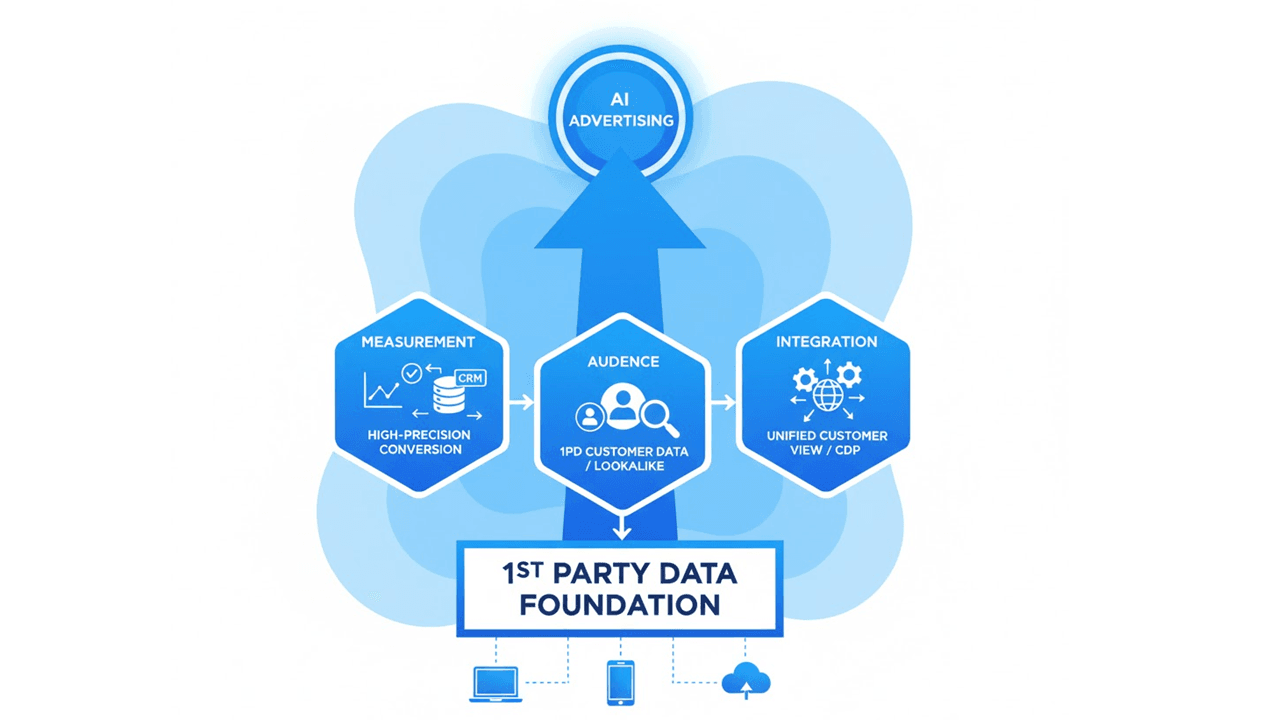
As Google Ads shifts to AI-first and the importance of its own properties increases, it is an absolute requirement for advertisers and media companies to develop a foundation to strategically collect and utilize their own first-party data (1st Party Data, 1PD) to achieve results in this new digital environment.
AI campaigns like PMax and Demand Gen demonstrate their true value when the 1PD provided by advertisers is used as audience signals. 1PD is the most valuable, clean "fuel" for the AI's learning model.
The foundational work companies must tackle immediately is as follows:
- 📊Thorough High-Precision Conversion Measurement: Accurate conversion data is essential for Google's AI bidding (Smart Bidding) to function. Utilizing technologies like Enhanced Conversions, customer lists including offline data from CRM and sales systems must be linked to Google Ads to provide high-quality feedback to the AI. Furthermore, it is necessary to set primary actions (Primary Action) and secondary actions (Secondary Action) according to the importance of conversion actions, clearly communicating optimization priorities to the AI.
- 👥Systematic Utilization of Audience Data: Utilize 1PD such as customer lists (Customer Match) and website visit history as audience signals for PMax and Demand Gen to accelerate the discovery of similar audiences (Lookalike audiences) by the AI.
- 🔗Promotion of Data Integration: Integrating customer data dispersed online and offline to establish a single customer view that comprehensively grasps "who, when, where, what, and why they did" is directly linked to improving personalization and LTV (Customer Lifetime Value).
This is equally important not just for advertisers, but also for media companies. 71% of publishers recognize 1PD as the key to advertising success, and they predict that the importance of 1PD monetization will further increase by 2026.
Conclusion: Investing in a CDP is the Shortest Route to Improving Results 💡
In the AI-driven advertising ecosystem, the ultimate solution for companies to maximize their data assets and establish a competitive advantage is the Customer Data Platform (CDP).
A CDP integrates all disparate customer data—from CRM, websites, apps, and offline purchase data—to create a persistent, single customer profile.
While traditional CRM primarily focuses on managing known customers and sales pipelines, a CDP centers on collecting and integrating first-party data, including online and offline behaviors, enabling the orchestration (integrated coordination) of customer experiences across diverse channels, including marketing, sales, service, and digital advertising.
What’s the difference? CDP vs CRM vs MA
CDP: Unifying customer data, overcoming CRM/MA limitations for strategic personalization.
A CDP like Antsomi CDP 365 is not just a data collection tool; it provides a Marketing Hub for utilizing integrated customer data across various touchpoints, including Digital Ads channels. This allows companies to generate high-quality audience segments to feed back into AI advertising, transforming them into data-driven enterprises.
As Google accelerates its shift to AI and 1PD, investing in a CDP is an essential management strategy to maximize digital marketing results and increase customer LTV over the long term. 📈
Terminology
Have Questions or Want to Learn More?
Contact us for more information about H+ CDP and how it can help your business.
Email us at: antsomi-contact@hakuhodody-one.co.jp
Or, fill out the form below and we'll get back to you shortly.